Azure DevOps
SmartGit integrates Azure DevOps workflows in various places, very similar to the GitHub integration. Some behavior can be customized by system properties.
Setup
To set up the Azure DevOps integration, go to Preferences, section Hosting Providers and use Add there. In the Add Hosting Provider dialog, have Azure DevOps selected and invoke Generate API token. This should open up your default web browser where you will have to confirm by Accept.
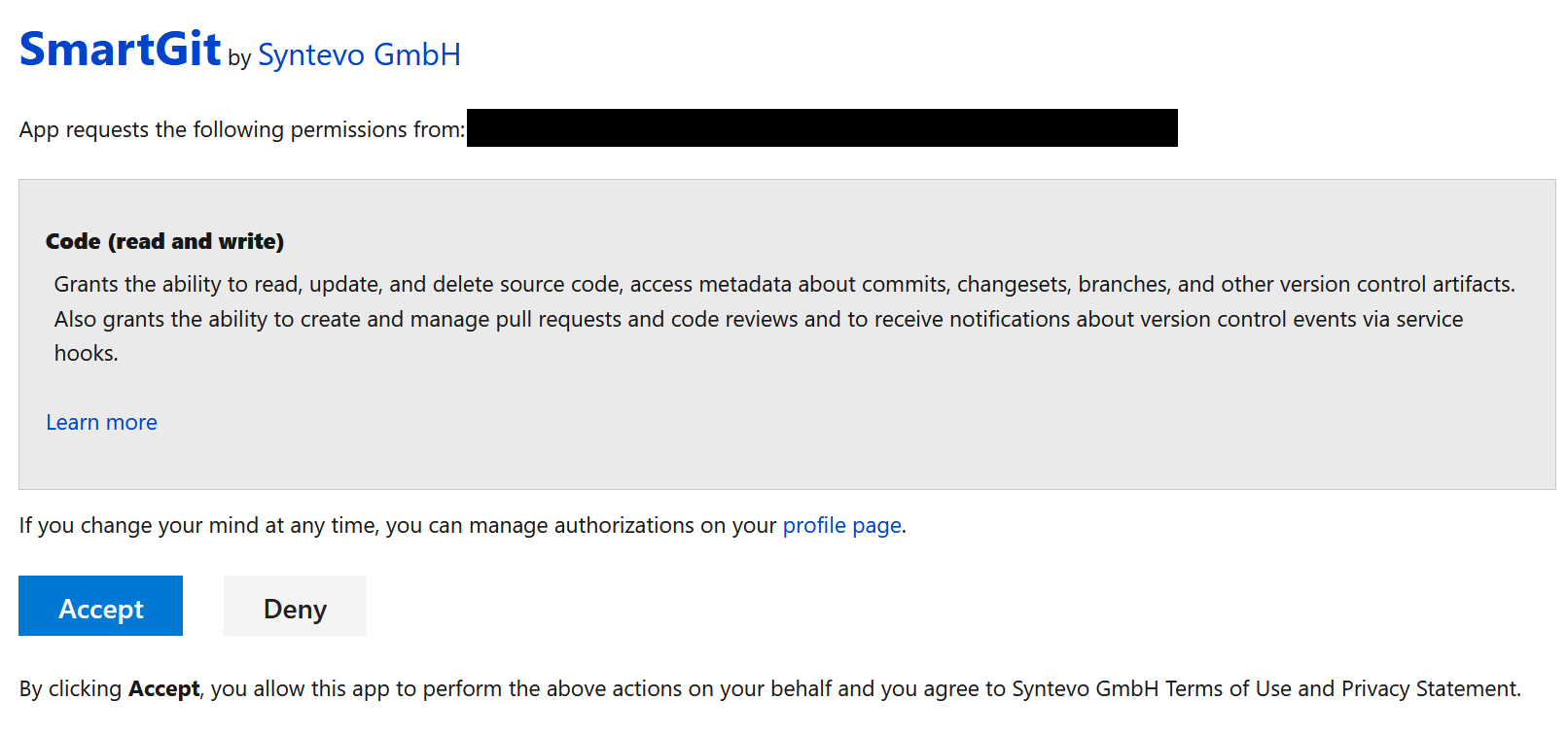
Once you have confirmed this page, you will be redirected to syntevo.com, where the generated access code will be displayed. Copy&paste this code into SmartGit’s Generate Token dialog and invoke Authenticate. The code will be used to create an application access token which will be used to populate the Token field.
By default, Use OAuth token for repository authentication will be selected. This will return the generated OAuth-token when Git asks for credentials (username + password) when connecting to your Azure DevOps repository. Using the OAuth-token has following advantages:
- its scope is more limited than plain password or possibly more powerful personal access tokens
- it will not require to create/enter a second set of credentials to SmartGit
Finally, confirm the Add Hosting Provider dialog using Add.
Note
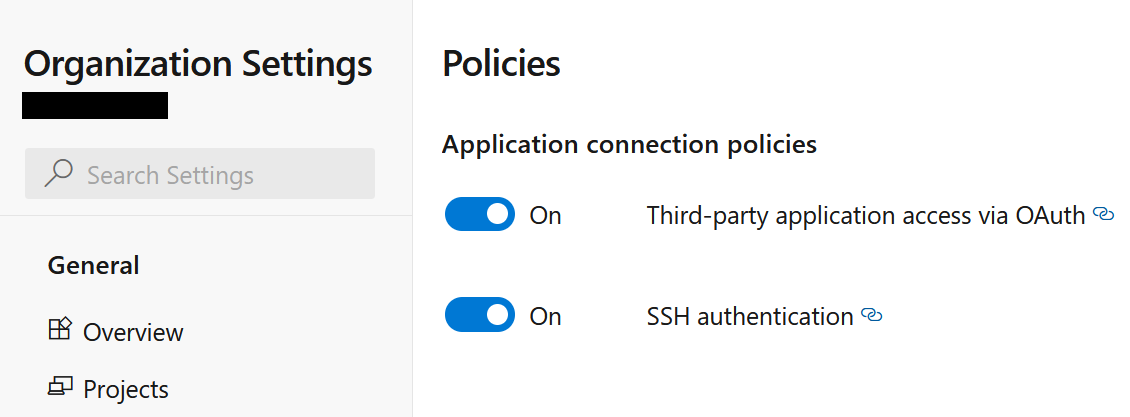
If above procedure fails make sure to allow Third-party application access via OAuth in your Organization Settings.
Re-setup OAuth
Sometimes you may need to rerun the OAuth setup, e.g. if a more recent version of SmartGit will request additional scopes. Usually, it’s sufficient to just open Preferences, section Authentication, open the Azure DevOps hosting provider and invoke Generate Token there. If this does not solve your problem, take following steps to rerun the OAuth setup from scratch:
- In SmartGit:
- get rid of all Azure DevOps-related credentials from Preferences, section Authentication
- get rid of the Azure DevOps hosting provider from Preferences, section Hosting Providers
- In Azure DevOps, open your profile from the top-right corner:
- Select “Manage Authorizations” there:
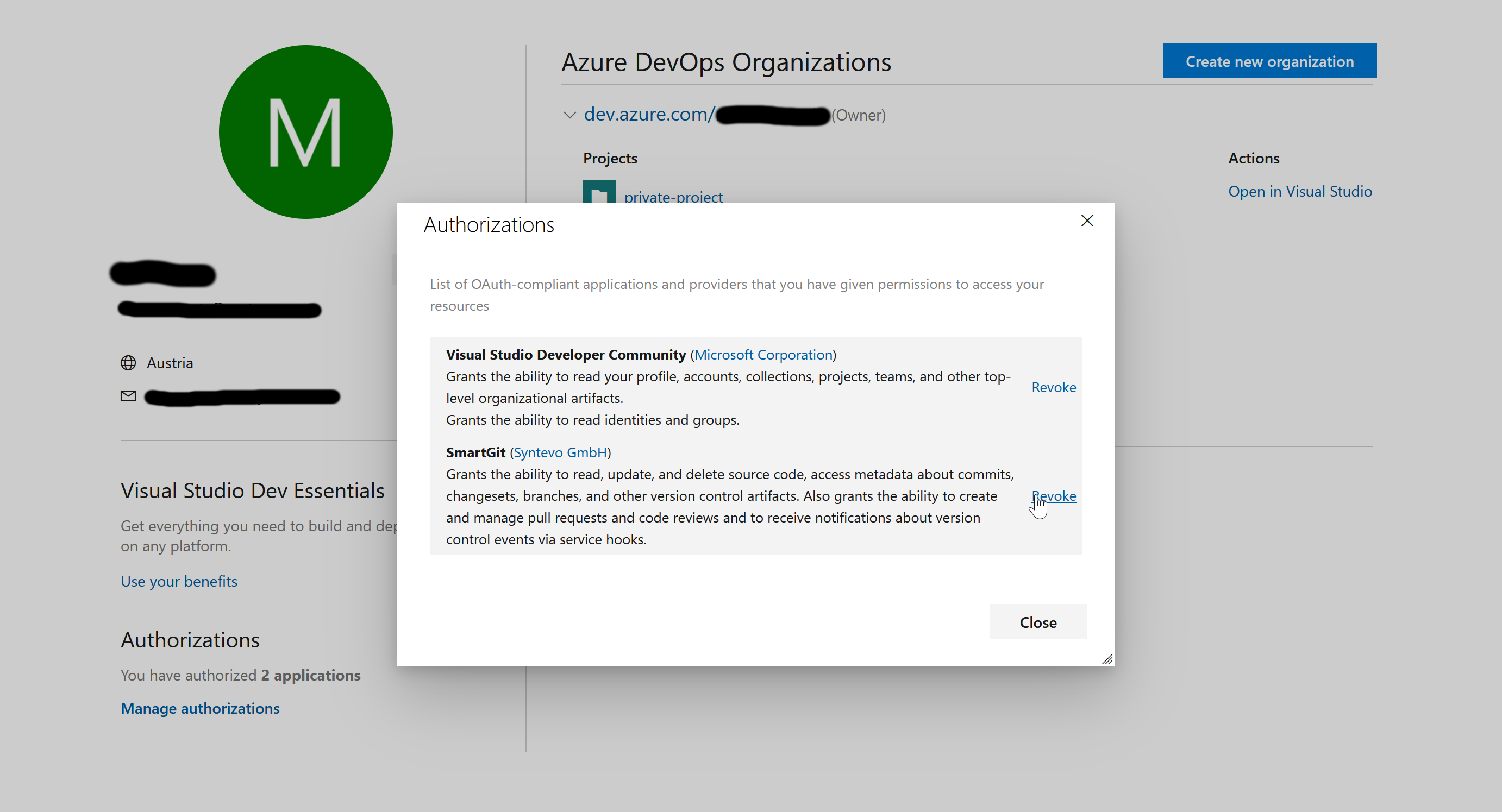
- Invoke Revoke for SmartGit
- Select “Manage Authorizations” there:
- In SmartGit, rerun through the OAuth setup again:
- open Preferences, section Hosting Providers
- Add a new Azure DevOps hosting provider, as described above
Setup with Multiple Accounts
If you have multiple Azure DevOps accounts, you can run through the above procedure for each of your accounts. This requires to login for every account in your web browser before invoking Generate Token.
To have the OAuth token to work for multiple accounts, Git has to request credentials per-repository. To check if the proper configuration is already set, invoke:
git pull
in your repository. If Git request credentials only for dev.azure.com, try to configure:
git config --global credential.dev.azure.com.useHttpPath true
Then run git pull again to confirm that Git will now ask for the complete repository URL.
Alternative setup using a personal access token
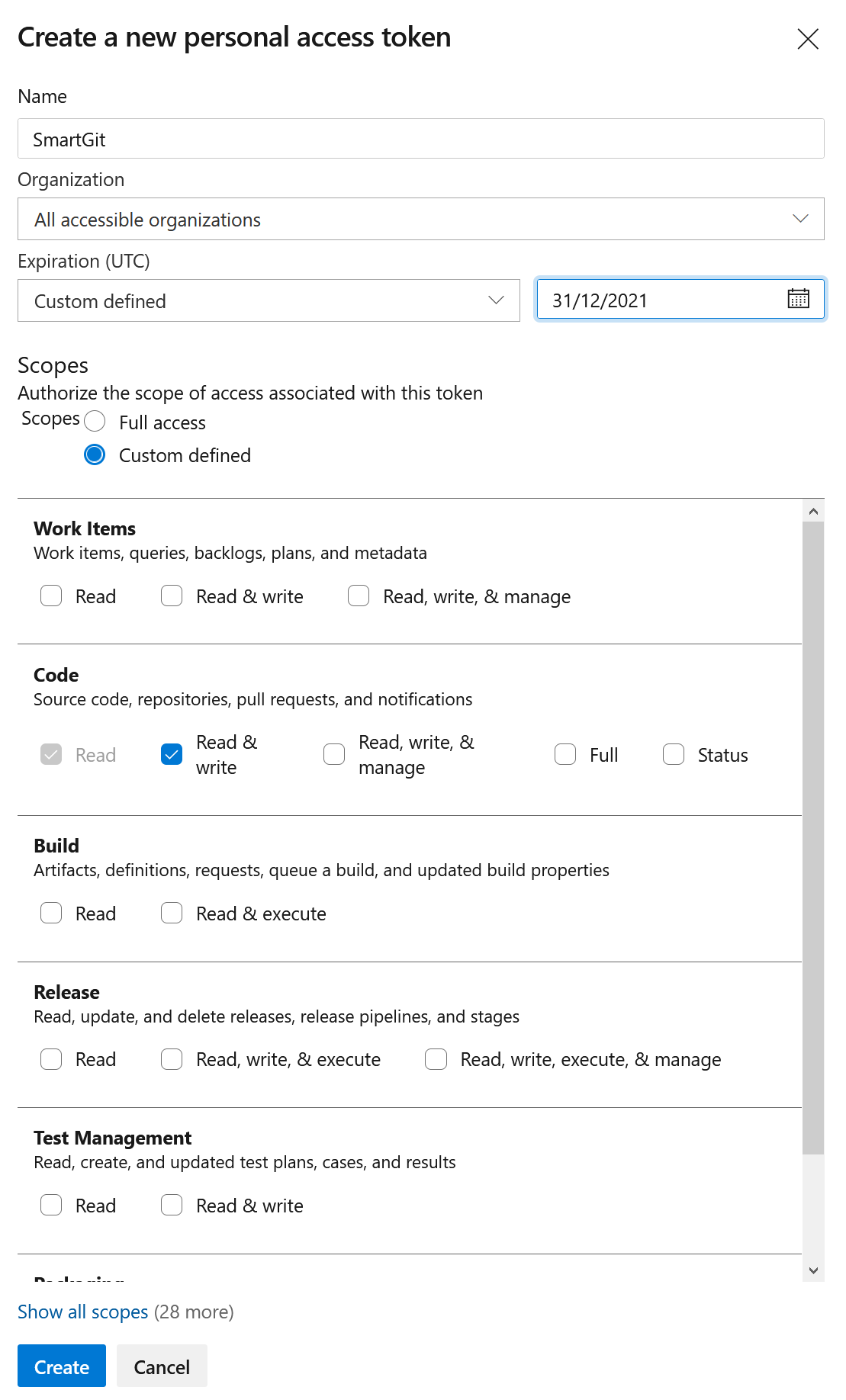
If OAuth is no feasible option for you, the Azure DevOps integration can alternatively be set up using a personal access token (“PAT”). Personal access tokens can be generated in the Settings area of the Azure web interface. For PATs to be usable by SmartGit, it’s important that Organization access is set to All accessible organizations (even if you just have a single organization). The scopes can be limited to Code - Read&Write.
Repository access using “Generate Git Credentials”
If you are just interested in accessing your Azure DevOps Git repositories, but you don’t need the additional Azure DevOps Hosting Provider functionality (like managing pull requests in SmartGit), you may open the Azure website, navigate to your Azure DevOps repository, invoke Clone and then Generate Git Credentials. When SmartGit asks you for User Name and Password enter these credentials.
Setting up a custom Azure DevOps Application for SmartGit
To get OAuth authentication working for Azure DevOps On-Premise instances or to avoid callbacks to https://www.syntevo.com you can set up a custom Azure DevOps application and configure SmartGit to use it for OAuth authentication.
Azure DevOps configuration
First, you have to create the application in your Azure DevOps profile. Click Create new application.

Then configure the application, with your custom Authorization callback URL and scopes Code (read and write) selected.
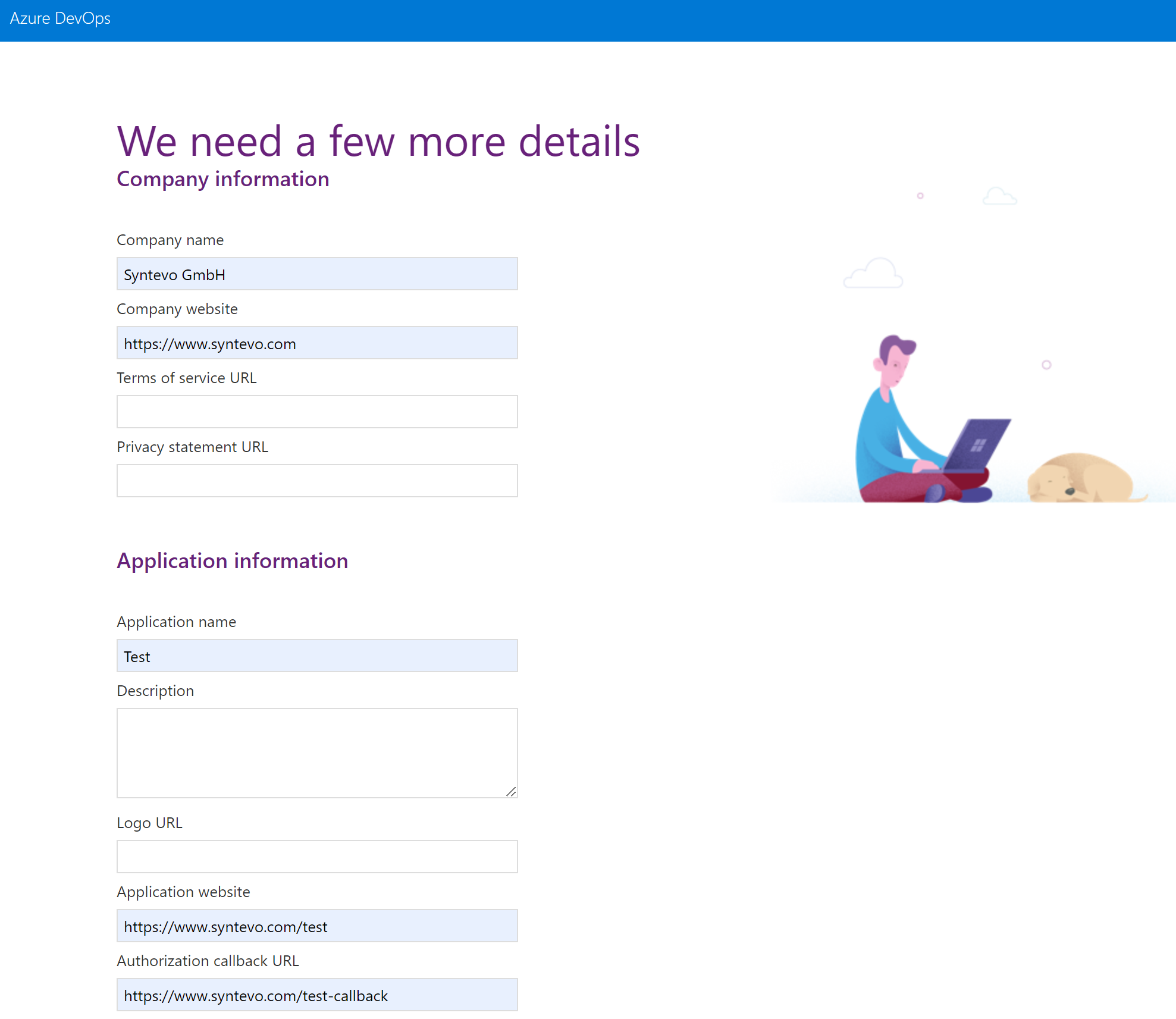
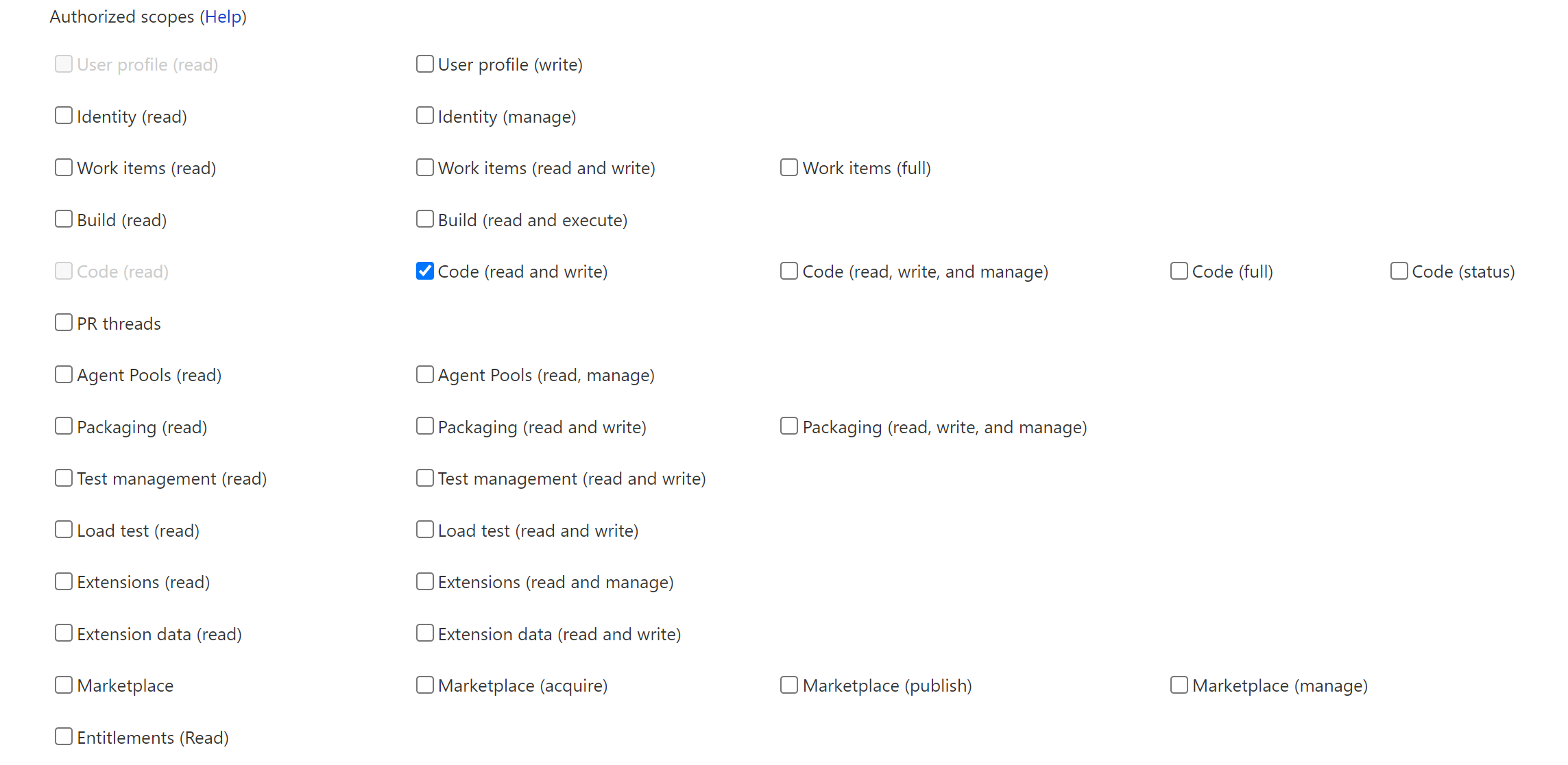
Once SmartGit initiates the OAuth authentication, Azure DevOps will return the initial code to the Authorization callback URL. The code will be passed as URL parameter code. This is what the user has to copy over to SmartGit’s Generate Token dialog.
Finally, confirm with Create Application. Next, Azure DevOps will display the application details.
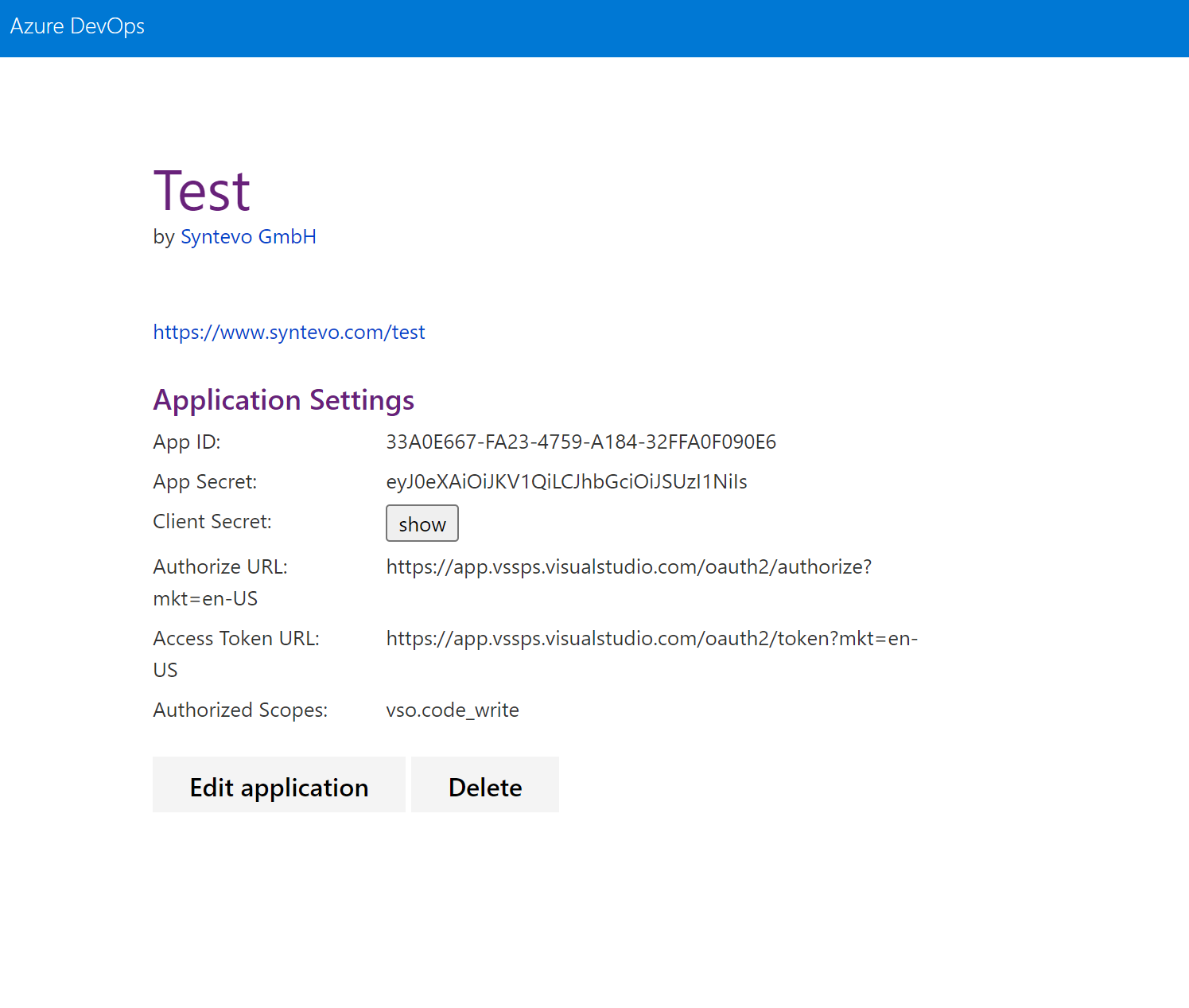
SmartGit configuration
Now SmartGit has to be configured to authenticate with this custom application. Add following lines to smartgit.properties (in SmartGit’s settings directory):
smartgit.azure.oauth.appId=33A0E667-FA23-4759-A184-32FFA0F090E6
smartgit.azure.oauth.clientSecret=eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsIng1dCI6Im9PdmN6NU1fN3AtSGpJS2xGWHo5M3VfVjBabyJ9.eyJjaWQiOiIzM2EwZTY2Ny1mYTIzLTQ3NTktYTE4NC0zMmZmYTBmMDkwZTYiLCJjc2kiOiJkNDAwYzIxYy02ODZiLTQ5NTctODg4Zi1kMTI5ZmY3MTc4ZWMiLCJuYW1laWQiOiJlMDY1YmIyYi0wMjc4LTYwMWMtOTc4Ny0zMGI2NGY0ZWI2MDMiLCJpc3MiOiJhcHAudnN0b2tlbi52aXN1YWxzdHVkaW8uY29tIiwiYXVkIjoiYXBwLnZzdG9rZW4udmlzdWFsc3R1ZGlvLmNvbSIsIm5iZiI6MTY1MTgzMTY1OCwiZXhwIjoxODA5NTk4MDU4fQ.jCcLR77IZtl56KS9KS39hrtHPm4d4HtUyCu_Xv4c9V1zNSuXMRTL49TP02OHoP6aXqtq7PWhKxEMBXTYdGMCPBMXoxLBPwEJTW7wCWTQH9AFHikZnpeqBjYwO18a7vg7u69Hm-kp-X_0-Vsdg1rTLojM-DwyAn0Ceb8FqYdnLXzgXl7D6c5Ux6GNVt5oA8wFDiQIEq-9paPgE2FbJKQ7yUroODNC4G7WzVsp41UKU8BOIN2YQgmMA8QSXdhxQsHfwgdVSrHCKkiGTBznJCXhmZkKkUkJ9QikXQ8s3FHBDormbJtT_m3Yx8fn24Vrm0_b7WV-Y9HdoZi1selRHTZU9Q
smartgit.azure.oauth.appCallback=https://www.syntevo.com/test-callback
Note, that clientSecret is actually the Client Secret from Azure DevOps, not the App Secret!