Commands
This page shows options influencing Git commands executed by SmartGit.
Note
Some highlighted options require an application restart to be applied.
Main Tab
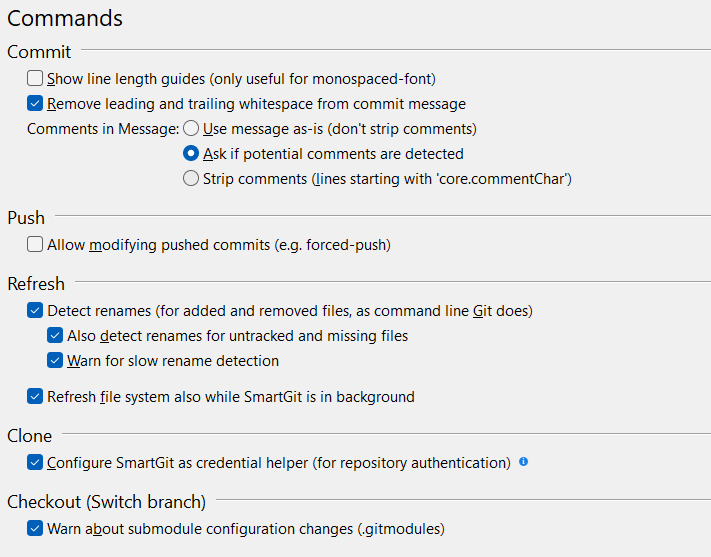
Commit
Allows you to configure how commits are handled. Here, you can set preferences for commit messages, such as whitespace handling and removal of comments.
Push
This allows you to modify a commit that has already been pushed to the remote.
Only select the Allow modifying pushed commits (e.g. forced-push) if you are sure you know Git well enough to understand the consequences of features such as forced push.
Refresh
Refresh settings control how your local file system will behave when synchronized from the remote.
With Detect Renames enabled, SmartGit will detect renames of added, removed, and optionally also untracked/missing file pairs.
Clone
If selected, SmartGit will replace the configured credential.helper in the .git/config of newly cloned repositories.
Executing remote Git commands (e.g. pull or push) in the terminal or a shell script will then use the credentials known to SmartGit.
Tip
The
Configure SmartGit as credential helpersetting is recommended if SmartGit is the only GUI client (along with using Git command line) used. This will simplify the authentication process when accessing platforms like GitHub. However, if you also use other GUI clients, using the SmartGit credential helper may disrupt the authentication of other GUI tools.
Checkout
The ‘Warn about submodule configuration changes’ option provides additional confirmation when working with Submodules (affecting the .gitmodules file)
Standard Window
This setting controls the level of detail and the complexity in the appearance of the Standard Window.
Log and Working Tree window
Commit View
This option configures the staging behavior when no files have been staged in the Commit View.
- Ask will prompt you how to proceed (Default)
- Commit all except untracked files will stage changes made to tracked files.
- Commit all including untracked files will stage changes to modified files, and will also stage any untracked files.
Commit Dialog
The ‘suggest’ options have the following behaviour:
- Add untracked files will suggest that new files not yet tracked will be added when staging a new commit.
- Remove missing files will suggest that previously tracked files which have been deleted from the working directory will be removed (
git rm).
Push
The Push settings allow for automatic tracking of new branches, and control over pushing of tags.
Stash
Select Automatically save stash on common commands to have SmartGit retry the execution of a Git command, if this failed and the working tree contains local changes. Select Include untracked files to include untracked files during a stash.
Refresh
Select Distinguish between content and EOL-only changes to specify how SmartGit will distinguish between content and end-of-line-only whitespace changes, in addition to the plain modified state reported by Git (in either case, files that Git considers as modified will be reported).
The EOL-change information will be displayed in the Files table State. If you want Git to ignore EOL differences (that’s usually the case if you are on Windows, which uses \r\n (crlf) as a line ending), consider using the .gitconfig setting
core.autocrlf = true
or using the text and eol attributes in a .gitattributes file to control EOL behavior.
Info
If you encounter problems with auto-stashing, e.g. SmartGit no longer shows a prompt, you may try to Restore all confirmation dialogs in section User Interface.
Log
The following options are available for the Log Window:
- Whether or not to allow all commands on stash and pull request commits
- Whether integration for Pull Requests and Review comments should be enabled for supported hosting providers such as GitHub
- Whether to allow multiple Log Windows for the same repository or file to be open concurrently.
Background Commands
Local and Remote Changes
Options on this page define which operations SmartGit can perform automatically when SmartGit is running in the background.
- Detect local changes in closed ‘favorite’ repositories - If this option is enabled, SmartGit will continue to monitor local changes to favorite repositories, even when they are closed.
- Detect remote changes will monitor remotes for changes. If this option is enabled, the following background monitoring options can be selected:
- Fetch Closed favorite repositories will
fetchfavorite repositories even when closed. - Fetch Open repositories when idle will fetch open repositories during periods of inactivity.
- Fetch Closed favorite repositories will
Note
Selecting Detect Remote Changes without also selecting either of the Fetch options, will enable SmartGit to poll the favorited remote Git repositories for changes at regular intervals. To avoid excessive overhead, only the lightweight
git ls-remotecommand is invoked, so you only get a notification about changes. The lightweight option does not detect all remote activities, for example, whether a currently checked out feature branch has been merged and removed. However, if Fetch closed ‘favorite’ repositories or Fetch open repositories when idle is selected, SmartGit also will perform fetch-operations which actually will fetch the changes from the remote repositories, which is more comprehensive in detecting changes, but is also more resource-hungry.
Garbage Collector
- Enabling the Periodically invoke Git’s garbage collection when idle to perform housekeeping optimizations in the background (such as
git gc), to reduce disk usage.
Git Executable
You can specify which Git Executable should be used by SmartGit.
- Bundled Git - This option uses the version of Git that comes bundled with SmartGit. This is the recommended setting.
- Other Git Executable - If you have an existing version of Git installed on your system, you can browse to locate the executable.
- The icon indicators display the Git and LFS versions and their compatibility with SmartGit (see note below). If the indicator shows a red cross, it means the selected Git executable is NOT compatible with SmartGit.
- Use SmartGit for authentication - This option will use the SmartGit credential helper for authenticating with remotes, and the Git
credential.helperconfiguration will be ignored. - Use pre-installed GitFlow - By default, SmartGit will use its own internal implementation of Git-Flow, however, set this option to instead use an existing GitFlow executable on your local computer.
Note
Git version requirements - SmartGit uses the selected Git executable for performing both local and remote activities. If the bundled Git executable is NOT used, some features in SmartGit may not function correctly. It is recommended that you keep your git executable version up to date to maximize your SmartGit experience.
Git Config
This tab-set allows you to edit your .gitconfig file, which controls a number of standard git settings. These settings will be applied as a default across all repositories. Please refer to the official Git config pages for details about each setting. However, you can also customize or override these settings at a per-repository level. Please refer to Repository Settings for further details.
Note
Advanced Users can also edit the Global and Repository-specific git configuration files directly using the Repository | Edit Git Config menu Option and then select the User or Repository option respectively.
Tip - Feature Branch Prefixing
For users who use a combination of Feature-Flow, Git-Flow or Git-Flow-Light, it is possible to provide a standard branch prefix across all 3 Development Processes through the following
.gitconfigsetting:
[smartgit "gui"]
prefixStartFeature = feature/
Authentication
SmartGit supports both SSH and HTTPS authentication to Git remotes.
SSH Client selection
The SSH options are only used if you use SSH to authenticate with remotes.
- Use system SSH client will use your existing system SSH client, and you will be responsible for managing keys on the local and remote server (e.g., as stored in the
~/.sshfolder). This is the recommended setting if you have an existing SSH setup and are comfortable with managing SSH keys and passwords. SmartGit will automatically re-use the system SSH credentials in this configuration.
Note
When using the system SSH client, it is necessary that the system SSH is configured so that it won’t prompt for any additional user input on the console. SmartGit is unable to interact with SSH prompts, and SSH operations may fail.
- Use SmartGit as SSH client simplifies access to remotes, as SmartGit will manage the complexity of encryption key pairs. This option is recommended if you interact exclusively with SmartGit and do not use the Git command line or other Git tooling when connecting to SSH repositories.
Note
The built-in SSH client requires the private key file to be provided in PEM format. Please see also the SSH-How-To.
SmartGit Credential Helper (HTTPS)
This section can be used to control the SmartGit credential helper when connecting to HTTPS repositories.
The SmartGit Password store
All passwords used to access repositories can optionally be stored in SmartGit’s password store. This password store is located in the
password file, found in SmartGit’s settings directory
(see Installation and Files).
The password store should be protected by a master password you provided, it should be changed if you have reason to believe it may become compromised.
- The Known credentials view shows all credentials stored in SmartGit.
- Credentials can be selectively removed, or all credentials can be removed. Removing a credential will force SmartGit to re-request credentials if you connect to the repository again.
- The Master Password for the password store can be set, reset, or changed through the Change Master Password dialog. It is highly recommended that you provide a master password to protect your remote credentials. Setting the new password to an empty (blank) string has the same effect as removing the master password.
Note
If you have forgotten the master password, you can use the command Edit | Preferences | Commands | Authentication | Change Master Password | Set new master password, without providing the existing password. However, this will cause all stored passwords to be discarded, and you will again be prompted for credentials when dealing with each repository.
Warning
The option NOT to provide a master password during installation (Don’t use a master password), or removing the master password by leaving the password blank is not recommended as this will leave passwords unprotected in plaintext.
- Ask for master password on startup will prompt you to prove the master password each time SmartGit is launched. If this option is not enabled, you will be prompted to enter the master password the first time SmartGit accesses the password store. The password will be remembered for the duration of the current SmartGit session.
