Authentication problems (push/pull fail)
This is a collection of common problems and resolutions related to authentication.
Preparation/general
log denotes directory inside the Settings Directory containing SmartGit’s log files.
While resolving authentication-related problems, it’s recommended to disable Detect remote changes option in the Preferences, section Background Commands to prevent background operations spoiling the log file with too many problems.
An independently opened terminal/shell refers to a terminal/shell which has not been opened through SmartGit:
- On Windows, you will usually just invoke
cmd.exefrom the Start-button. - On Linux or macOS, open a terminal
Error: Authentication failed for ‘…’
Step “Check Command”
Check the Output view or the log-directory for the exact command which fails and try to invoke the command from an independently opened terminal/shell.
- If the command works there, continue with step “Check Git-Shell”.
- Otherwise, check whether the access URL is actually correct and your credentials are correct.
- If they are definitely correct, continue with step “Check Credential Manager”.
Step “Check Git-Shell”
Open a Git shell from within SmartGit: right-click the offending repository in the Branches view and invoke Open Git-Shell and try to invoke the command from this shell.
- If the command works there, continue with step “Check Hosting Provider”.
- If the command does not work there
- if you are on Windows, continue with step “Check Git Credential Manager”.
- continue with step “Check Environment Differences”.
Step “Check Hosting Provider”
SmartGit’s Hosting Provider configuration may interfere with the authentication.
- If your repository is connected to GitHub, Bitbucket or another hosting provider, known to SmartGit, open the Preferences, select section Hosting Provider and get rid of the corresponding hosting provider there.
Then retry.
- If the command works there, re-setup the hosting provider in the Preferences again and retry
- if it stops working again, continue with step “Contact Support”.
- If the command does not work without the hosting provider configured, continue below.
- If the command works there, re-setup the hosting provider in the Preferences again and retry
- If your repository is connected to GitHub, check whether this problem might be related to organization access.
- If you are not connected to a hosting provider
- if you are on Windows, continue with the next step.
- continue with step “Check Firewalls/Antivirus tools”.
Step “Check Windows AutoRun”
Command Processor AutoRun scripts may interfere with SmartGit’s authentication hook.
Open the Windows registry and check whether for key HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Command Processor the value AutoRun is configured.
- If not configured, continue with the next step
- Otherwise, temporarily rename the
AutoRunscript toAutoRun~and see whether authentication works now.- If it works now, consider to permanently disable the AutoRun script or enable Git’s credential manager.
- If it still does not work, leave
AutoRun~renamed and restart with step “Check Command”.
Step “Check Firewalls/Antivirus tools”
SmartGit is configuring Git with a small utility tool for password callbacks.
Once invoked by Git, this tool is connecting to SmartGit using sockets to receive credentials.
Firewalls/Antivirus tools may block this socket communication.
This can been seen in the injector log files which will show up a java.net.ConnectException.
- Make sure that SmartGit’s executables (on Windows all files in the
bin\-subdirectory) are not blocked from opening a local socket or connecting to a local socket - If this does not help, continue with the next step.
Info
Sometimes firewalls/antivirus tools will only block SmartGit processes sporadically. In this case, you may see unexpected, redundant “Login” prompts. For details, see below.
Step “Check Credential Manager”
If you are on Windows and SmartGit as well as command line Git client simply fails without asking you for a password,
- open the Windows “Credential Manager”, check for possible Git credentials there and get rid of them, then try again to pull/push (from command line)
-
If this still does not help, this may be due to a problem in the Git-Windows credential handling. You may check by temporarily disabling the system credential helper using following command:
git config --global --unset credential.helperand invoke the pull/push again.``- if this solves the problem, consider to report this problem to the Git mailing list: https://git.wiki.kernel.org/index.php/GitCommunity
- if this does not solve the problem, continue with step “Contact Support”.
Info
Depending on your system configuration,
credential.helpermay be configured in your repository’s.git/configinstead of the global.gitconfig, so you might have to remove it from there. One of our users has reported that Microsoft Git Credential Manager was immediately resetting the configuration tomanager, so it was necessary to uninstall this tool first.
Step “Check Environment Differences”
Compare environment variables of the independently opened terminal/shell and the Git-Shell for possible differences
- If this gives you a clue on what the problem is, please drop us some lines at [email protected]
- If you can’t figure out the reason, continue with step “Contact Support”.
Step “Contact Support”
Send us a detailed description of the problem, including:
- the problem resolutions you have already tried,
- output of environment variables you have compared,
- the zipped
logdirectory
Error (GitLab): Could not read from remote repository: the project you were looking for could not be found
Go to your GitLab server configuration page (or ask your administrator to do so) and make sure that you have been granted all necessary access rights. You may start off with granting all possible rights and step-by-step reduce rights as long as you can still pull and push to the offending repository.
- If you can’t get the access problem resolved, continue with step “Contact Support”.
Error (Bitbucket): Server returned HTTP response code: 400 for URL: https://bitbucket.org/site/oauth2/access_token
On the setup of the Bitbucket hosting provider, SmartGit has retrieved a “refresh” token which it is using subsequently to request short-lived “access” tokens. Under certain circumstances, this refresh token may become invalid. In this case, it will be necessary to recreate the hosting provider: go to the Preferences, section Hosting Provider, get rid of the Bitbucket hosting provider an re-Add the hosting provider.
- If this still does not resolve your problem, continue with step “Contact Support”.
Error (GitHub): Repository not found
Check the Output view or the log-directory for the exact command which fails and try to invoke the command from an independently opened terminal/shell.
- MacOS: If the problem is still present there and you are not even asked for credentials, you may have to update your credentials in the Keychain. If you want SmartGit to authenticate using OAuth, make sure to delete the credentials there.
Error: credential-cache unavailable; no unix socket support
This indicates a problem with the “manager” credential helper.
You may try to disable the credential helper by executing git config --global --unset credential.helper from a command shell.
Then invoke the pull/push again.
See also Step “Check Credential Manager”, above.
Error: “invalid credential line” when pushing (or pulling)
If you encounter an “invalid credential line” error (the Push operation may still succeed),
this may be due to unintended output in shell profile files, such as ~/.profile.
Removing unnecessary output-producing commands from these files may resolve the issue.
SmartGit only stores one pair of credentials for a single domain (e.g. github.com)
If:
- SmartGit fails to access a repository on a domain for which you have another repository working;
- and you actually have to use different credentials for both repositories
this might be caused by having configured a Git credential.helper (probably in your global .gitconfig or in the system-wide .gitconfig).
To resolve, you may set useHttpPath option, see https://git-scm.com/docs/gitcredentials.
Windows: Reoccurring “Login” prompts, usernames/passwords seems to become lost frequently
If you are receiving frequent “Login” prompts even your username/password haven’t changed and you always tell SmartGit to store username/password, this may be caused by antiviral/firewall tools which are interfering the connection between the main SmartGit process and credential-helper processes. To resolve, try to exclude following executables from inspection by your antiviral/firewall tool. This is usually done by adding them to some trusted applications list:
-
<smartgit-installation>\bin\smartgit.exe -
<smartgit-installation>\git\bin\git.exe -
%SystemRoot%\Windows\System32\cmd.exe
Details on the interaction between SmartGit and Git’s credential manager on Windows
If you have credential.helper=manager configured on Windows, Git will first invoke special code which tries to retrieve the password from the Windows Credential Manager.
- If the correct credentials are stored there, it’s fine.
- If not, Windows will ask for credentials:
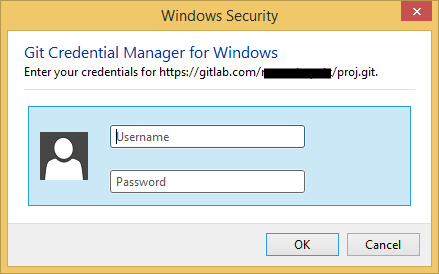
- If you will enter the correct credentials there, it’s fine.
-
If you will enter wrong credentials there, the dialog will show up again (back to step 2, this happens a couple of times).
Up to this point SmartGit was not involved in the credentials prompt at all.
- If you cancel the dialog, Git will invoke the
GIT_ASKPASSenvironment variable callback which is set by SmartGit. - If the correct credentials are stored in SmartGit, they will be returned.
- Otherwise, SmartGit will show its own credentials dialog:
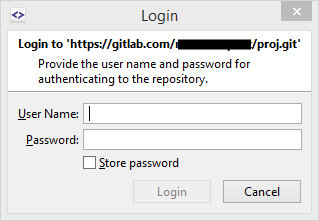
- If you will enter the correct credentials there, it’s fine.
-
If you will enter wrong credentials there, the dialog will show up again (back to step 7, this happens a couple of times).
In either case, the credentials returned by SmartGit will be stored in the Windows Credentials Manager, too. Hence, subsequent requests for these credentials will be served directly from the Credentials Manager (step 1).
http(s)-Passwort is asked again after restart
A user reported that on his Linux system with older Git 1.8.3.1 he entered https passwords and told SmartGit to store it, but after a restart he had to re-enter them. Building Git from sources and using that (here: latest version 2.27) solved this problem.
Debug logging: enable injector logging
To intercept Git credential prompts, SmartGit is “injecting” callback scripts. To enable debug logging for these scripts, perform following steps:
- Add following line to
smartgit.properties, which is located in the settings directory:
smartgit.injectorLogging=true - Restart SmartGit
- Retry the failing operation
- Once the problem has occurred again, shutdown SmartGit
- Backup all
smartgit-http-*andsmartgit-ssh-*files from the settings directory. Also includelogs/log.txt.0. - Upon request from us, compress these files, including the
logdirectory and send them [email protected]
