Jira
The SmartGit integration to Atlassian Jira allows you to select a commit message (including the Jira issue id) directly from open Jira issues, and optionally mark issues as resolved on Push.
Prerequisites
Jira integration is only available with commercial licenses and will only be present if Bugtraq configuration has been set up correctly to your Jira server.
The Jira integration is only available for commercial licenses and will only be present if Bugtraq configuration has been set up correctly to your Jira server.
Note
When connecting to a cloud-based Jira instance (*.atlassian.net), login with your username, not your email address. You can find your username in your profile (top-right corner).
Authentication with API
Depending on your Jira version (server vs. cloud), authentication may require:
- Using your username and password, or
- Creating an API token.
To create an API token, open your Jira account and select Security settings.
Tip
For Jira Cloud, you can find security settings at: https://id.atlassian.com/manage-profile/security
In the API token section, select Create and manage API tokens, then Create API token. Assign a label (e.g., SmartGit”) and confirm with Create.
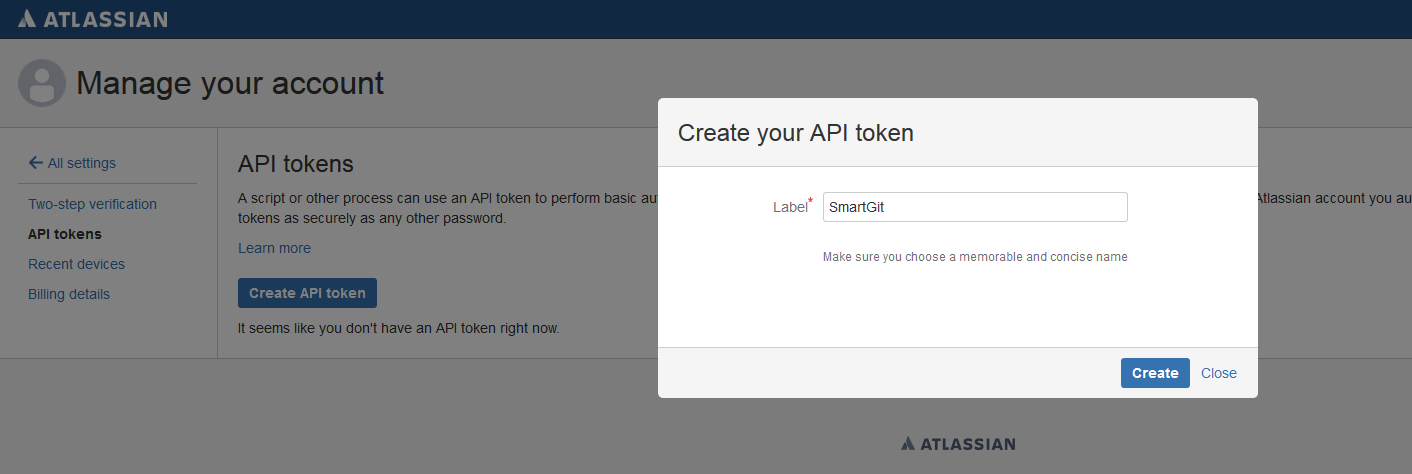
In the next dialog, invoke Copy to clipboard. The token will then appear in the list.
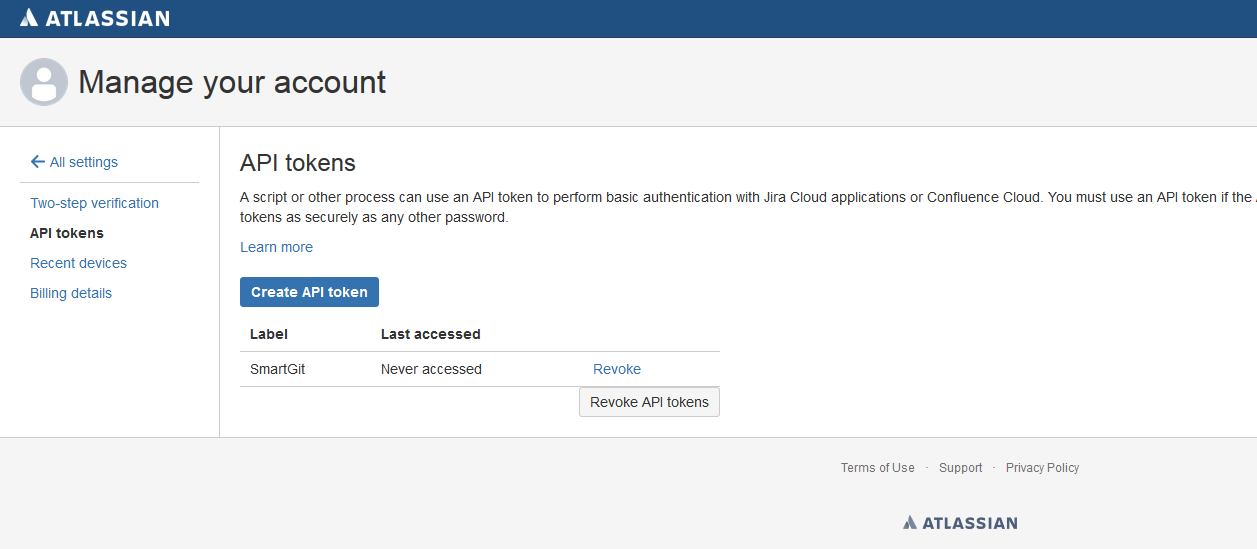
You can now authenticate SmartGit with Jira using your email address as the User Name and the Api token as the Password.
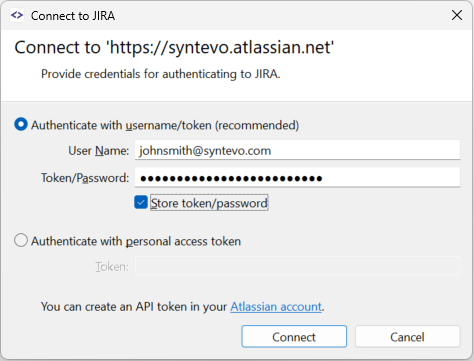
Note
It is recommended to store the API token in the SmartGit Password Store by selecting Store token/password.
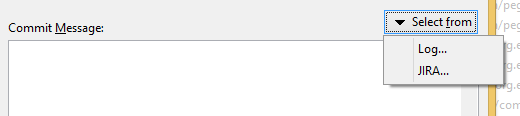
Commit Message Selection
Commit message selection from Jira is available in the Commit and Edit Last Commit Message commands in the Commit View, as well as in some interactive rebase commands in the Journal view.
Resolving on Push
For all Push operations (except Push To), SmartGit checks the pushed commits for affected Jira issues and offers to mark them as resolved, provided a suitable transition exists (see the Example below).
A Jira issue is considered affected if:
- It is mentioned in at least one commit message of the local branch commits being pushed, and
- It is not mentioned in any commit message of the remote branch commits being replaced, and
- When using Git-Flow, you are not pushing into a feature or a hotfix branch (SmartGit will instead ask whether to resolve such commits when finishing the feature or hotfix,
i.e., integrating into
developormaster), and - The issue is resolvable (i.e., there is at least one transition available that moves the issue into a resolved state.
Note: Not all issues are resolvable—for Example, issues that are already resolved or closed.
Example
In Jira’s classic workflow, an issue that is in progress can be resolved or closed. When such issues are mentioned in a commit message, SmartGit offer will to resolve them, as transitions are valid during a push. On the other hand, issues already resolved or closed can only be reopened.
If such issues are mentioned in a commit message, SmartGit will not offer any resolution.
Tip
You can disable the Resolve-check in Preferences → **Low-Level Properties** by configuring jira.resolveOnPush.
Custom workflows
SmartGit supports default Jira workflows for detecting resolvable issues. If you use a custom workflow, you may need to define resolvable states manually using Low-Level Properties.
Note
SmartGit will only offer issue resolution if your Jira credentials are correctly configured.
To confirm, use Select from Jira and enter your credentials.
You can completely disable this functionality using Low-Level Properties.
Support for ‘commit.template’
The Jira integration respects the Git commit.template configuration. The following keywords are replaced with the corresponding Jira issue attributes:
%BUGID%%BUGSUMMARY%%BUGDESCRIPTION%
Miscellaneous
Jira connection configurations are stored in bugtracker.yml, in the Settings directory.
Referenced passwords are stored separately in passwords.
Solutions to troubleshoot potential problems
“No project could be found with key ‘…’” or “The value ‘…’ does not exist for the field ‘project’”
In Jira Cloud, after authenticating successfully with a token, subsequent requests may behave unexpectedly if the token is later removed.
Using curl demonstrates the behavior:
- With an invalid token, authentication fails as expected with HTTP 401 Unauthorized:
$ curl -I -H "Authorization: Basic bWFyYy5zdHJhcGV0ekBzeW50ZXZvLmNvbTpYcVF6ZFdFMGUxRUw1VmM2ZjRmWDY0MjQ=" https://yoursite.atlassian.net/rest/api/2/project/PROJECT/versions
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
- With a valid token, authentication succeeds with HTTP 200 OK:
$ curl -I -H "Authorization: Basic bWFyYy5zdHJhcGV0ekBzeW50ZXZvLmNvbTpIZk9rdjhHNDdZMjlLZEl0ZmczYkYxQ0I=" https://yoursite.atlassian.net/rest/api/2/project/PROJECT/versions
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
- After the token is deleted in Jira, authentication may still succeed temporarily (due to caching):
$ curl -I -H "Authorization: Basic bWFyYy5zdHJhcGV0ekBzeW50ZXZvLmNvbTpIZk9rdjhHNDdZMjlLZEl0ZmczYkYxQ0I=" https://yoursite.atlassian.net/rest/api/2/project/PROJECT/versions
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
- Later, Jira returns HTTP 404 Not Found, which SmartGit interprets as a valid token with a non-existing project:
$ curl -I -H "Authorization: Basic bWFyYy5zdHJhcGV0ekBzeW50ZXZvLmNvbTpIZk9rdjhHNDdZMjlLZEl0ZmczYkYxQ0I=" https://yoursite.atlassian.net/rest/api/2/project/PROJECT/versions
HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found
Solution
- Shutdown SmartGit
- Remove the corresponding configuration from
bugtracker.yml(see above) - Restart SmartGit
SmartGit will then prompt for new credentials.
